Неврология
Кафедра Неврологии в Медикал Паркe предлагает полный диапазон специализированных неврологических услуг, а также специалистов, приверженных оказанию современной, ограждающих помощи.
Медикал Парк Неврологии и Нейрохирургии Медицинского Центр возглавляeтся всемирно признанными специалистами, которые являются экспертами в диагностике и лечении наиболее сложных заболеваний мозга и позвоночника.
Инсульт
Головная боль
Эпилепсия
Двигательные нарушения
Нарушение памяти
Гидроцефалия
Альцгеймер
Бессонница
Нервно-мышечные проблемы
наши пациенты могут обратиться за консультацией к врачу.
Кроме того, нашим пациентам доступно дистанционное второе мнение о неврологических состояниях и нейрохирургических услугах, после того, как вы отправите нам свои медицинские отчеты, наши эксперты оценят ваши отчеты и диагностический тест и вам будет предоставлена письменная рекомендация относительно ваших планов лечения.
Медикал Парк признан 10-м в Мире Самым Лучшим Центром в Хирургии по Болезни Паркинсона.
Метод применяемый в хирургическом лечении Болезни Паркинсона и других нарушений , составляет 80%.
Успех-это не случайность!
-
• Продвинутый нейрорадиологические отображение систем
-
• Последние Первоклассные научные методы обработки
-
• Высококвалифицированные академические врачи
В Kлинике Нейрохирургии Больницы Медикал Парк , в Взрослых и Педиатрических Случаях;
-Опухоли Головного Мозга
-Тремор Хирургии
-Спинная Хирургическая операция и другие методы особого отношения применены…



Xирургия Позвоночника
Старение, неправильная механика тела, травмы и структурные аномалии могут повредить ваш позвоночник, что приводит к боли в спине и другим симптомам, таким как боль в ногах и/или онемение или даже слабость ноги.
Основной целью операции на спине или шее является коррекция анатомического поражения у лиц, которые не показывают улучшения при консервативном (нехирургическом) лечении. Хирургия не является вариантом для пациентов, когда анатомическое поражение, объясняющее их боль, не может быть идентифицировано.
Операция полезна только для изменения анатомии пациента (например, удаление грыжи диска). Почти никогда нет оснований считать исследовательскую операцию «поиском» причины боли.
Наиболее важным фактором в определении успеха операции на позвоночнике является правильная предоперационная диагностика. Без точного предоперационного диагноза даже самая технически успешная операция имеет мало шансов на успешный исход.
Spine surgery can basically accomplish three tasks:
1. Decompress a nerve root or the spinal cord
2. Stabilize an unstable or painful segment with spinal fusion surgery
3. Reduce a deformity (e.g. scoliosis surgery in the thoracic spine)
Common surgical procedures
There are a number of conditions that may lead to spine surgery. Common procedures include:
-
Discectomy or Microdiscectomy: Removal of a herniated intervertebral disc. Therefore, removing pressure from the compressed nerve. Microdiscectomy is a MISS procedure.
-
Laminectomy: In this procedure, a surgeon removes parts of the bone, bone spurs, or ligaments in your back. This relieves pressure on spinal nerves and can ease pain or weakness. It can make your spine less stable. If that happens, you'll probably need a spinal fusion. Doctors sometimes do the two procedures together.
-
Laminotomy: Removal of a portion of the vertebral arch (lamina) that covers the spinal cord. A laminotomy removes less bone than a laminectomy.
Both laminectomy and laminotomy are decompression procedures. “Decompression" usually means tissuecompressing a spinal nerve is removed.
-
Foraminotomy: Removal of bone or tissue at/in the passageway (called the neuroforamen) where nerve roots branch off the spinal cord and exit the spinal column.
-
Disc replacement: As an alternative to fusion, the injured disc is replaced with an artificial one.
-
Spinal fusion: This is the most common surgery for back pain. The doctor will join spinal bones, called vertebrae, together. This limits the motion between them and how far your nerves can stretch. But it probably won't limit your activity. It's rare, but the bones don't always fuse completely. A surgical technique used to join two vertebrae. Spinal fusion may include the use of bone graft with or without instrumentation (eg, rods, screws). There are different types of bone graft, such as your own bone (autograft) and donor bone (allograft). A fusion can be accomplished by different approaches.
Parkinson's Disease
Brain pacemakers are complex electronic devices that have become increasingly popular in recent years in the surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease as well as a number of other movement disorders.
Gamma Knife Radio Surgery
Gamma Knife is a bloodless surgery for intra-cranial tumors and cerebral diseases without need to conventional surgery. Neurosurgeons use this method alone or along with microsurgery for eligible patients and diseases. Our team started performing Gamma Knife surgery on February 25, 1997. Prof. Türker Kılıç, M.D., is the first Turkish medical doctor to have radiosurgery training at Karolinska Institute, Sweden. Gamma Knife enjoyed gains from technological advanced and the methodology is still preferred by neurosurgeons worldwide. There are approximately half million people, who are treated with Gamma Knife Surgery worldwide. Approximately 1.6% of all those patients had been treated by your team. From this perspective, our team is among first five Gamma Knife units with highest case number.
Bloodless Surgery
Gamma Knife is an extremely sensitive and efficient device, also referred as radiosurgery, which uses radiation beams to treat intracranial tumors. Neurosurgeons, using this modality, focus radiation beams directly and accurately to the target area, with no negative influence on intact surrounding tissue. Radiosurgery enables neurosurgeons focus radiation beams directly and accurately to the target area, with no negative influence on intact surrounding tissue.
Studies demonstrated that Gamma Knife surgery has high success rate. For instance, a tumor at any localization in the brain can be controlled by >85 % (or in other words, tumor is successfully debulked). This modality is referred as Gamma Knife, since the radiosurgery (single-session treatment) has accurate efficiency on the target area and resultant changes are “surgical" in nature. However, no blade or scalpel is used, on the contrary to the name of the method. Therefore, this surgery is scalpel-free and bloodless and the complication risk is very low.
Use of three-dimensional computer-assisted planning and absolute immobility of the patient minimize delivery of radiation beams to intact brain tissue.
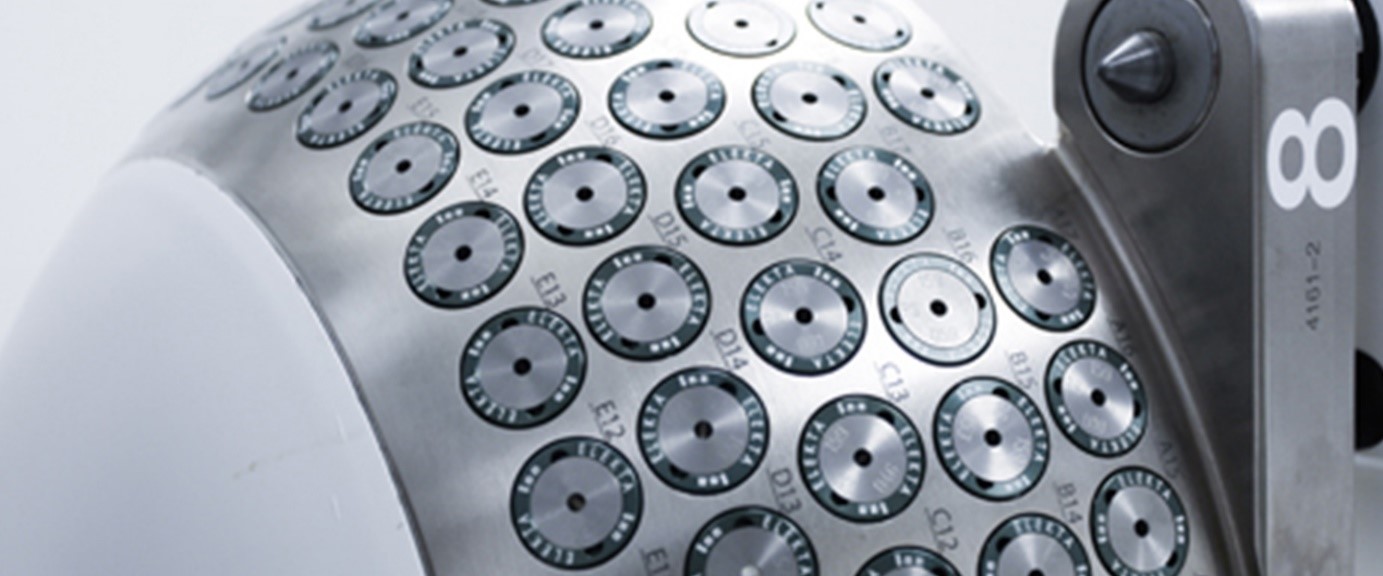
Approximately 200 cobalt-60 sources are loaded in each treatment unit. Those sources may generate thousands of beams, as thin as approximately a hair, at a very high sensitivity level (greater than 0.5 mm). Such beams are weak enough to have no hazardous influence of normal tissue through the tract to the target. However, when they are accurately focused on the target, beams merge in order to be sufficient for treating the target area.
On the contrary to multiple visits for linear accelerator (LINAC) therapies (fractional therapy) which use lower fractional doses, whole therapeutic dose can be given in single session, since Gamma Knife radiosurgery is extremely sensitive. Minimization of radiation dose is important for everybody, but especially for patients with cancer who are already maintained on other radiotherapy options. If low-sensitivity therapies are used for such patients, treatment may take up to 6 weeks for metastatic brain tumor, which implies a cancer spreading from the primary focus to other body parts.

